Vue实战:利用自定义指令实现鼠标拖动元素效果
本篇文章分享一个Vue实战,介绍下使用Vue的自定义指令实现鼠标拖动元素的效果以及解决移动端适配的问题。
核心属性
Element.clientWidth:元素可视宽度。Element.clientHeight:元素可视高度。MouseEvent.clientX:鼠标相对于浏览器左上顶点的水平坐标。MouseEvent.clientY:鼠标相对于浏览器左上顶点的垂直坐标。Touch.clientX:触点相对于浏览器左上顶点的水平坐标(移动端属性)。Touch.clientY:触点相对于浏览器左上顶点的垂直坐标(移动端属性)。HTMLElement.offsetLeft:当前元素左上角相对于父节点(HTMLElement.offsetParent)的左边偏移的距离。当元素脱离文档流时(position: fixed)则相对于原点(浏览器左上顶点)偏移。【相关推荐:vuejs视频教程】HTMLElement.offsetTop:当前元素左上角相对于父节点(HTMLElement.offsetParent)的顶部偏移的距离。当元素脱离文档流时(position: fixed)则相对于原点(浏览器左上顶点)偏移。Element.style.top:可读可写,值为offsetTop。Element.style.left:可读可写,值为offsetLeft。
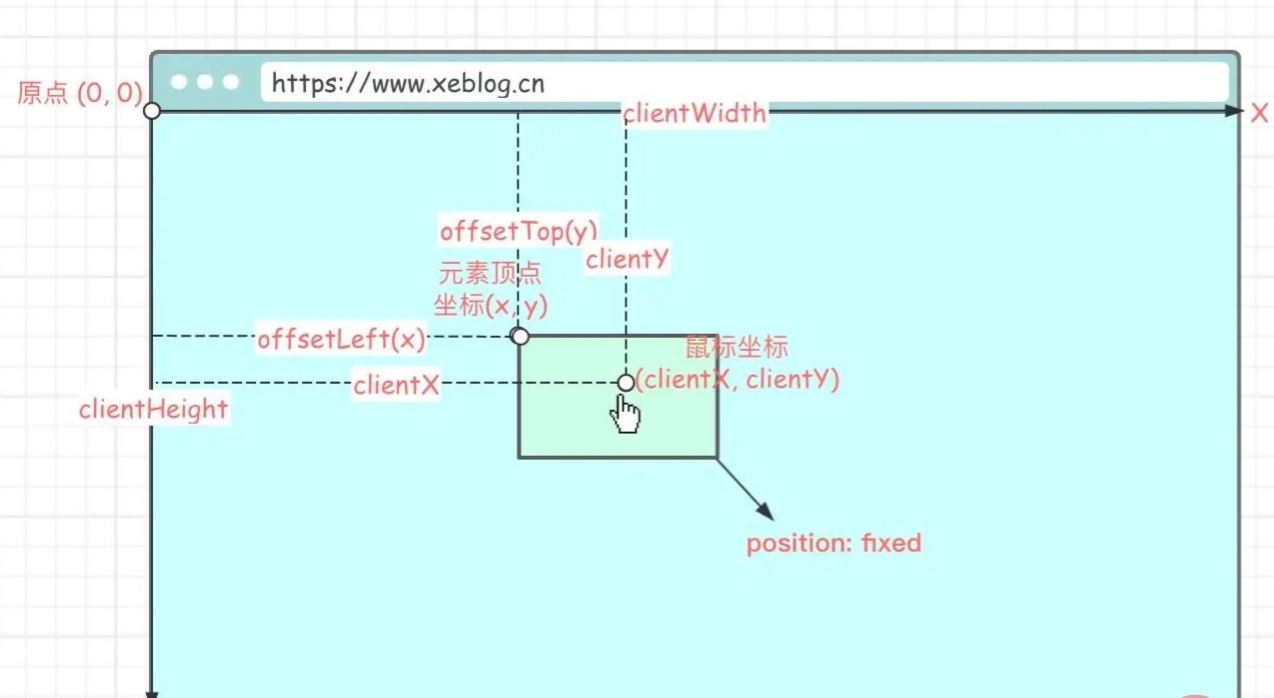
实现思路
待滑动元素必须设置
position: fixed or absolute
元素滑动需要依赖于鼠标的移动,鼠标的移动位置决定了元素滑动的位置,元素的位置是通过调整左上顶点坐标来的,所以我们要知道元素滑动后的左上顶点坐标,这样才能将元素移动到指定位置(鼠标悬停的位置)。
首先要计算出鼠标在移动元素前相对元素的位置 (x, y) :
// 鼠标当前的位置减去元素当前的位置 (x, y) = (e.clientX - el.offsetLeft, e.clientY - el.offsetTop)
鼠标相对元素位置是指相对于元素左上顶点的位置。
e 指鼠标事件,el 指滑动的元素。
知道了鼠标的相对位置,后续的鼠标移动,只要知道移动后的鼠标坐标,就能很容易的把元素的左上顶点坐标算出来。
计算元素移动后的左上顶点坐标 (x', y') :
// 鼠标当前的位置减去滑动前的相对位置 (x‘, y’) = (e.clientX - x, e.clientY - y)
(x', y') 就是要移动的最终坐标,然后调整元素位置即可
el.style.left = x' + 'px' el.style.top = y' + 'px'
代码
<template>
<div class="ball-wrap" v-drag @touchmove.prevent>
<!-- 省略... -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
isDrag: false
},
methods: {
click() {
if (this.isDrag) {
return
}
// 省略...
}
},
directives: {
drag(el, binding, vnode) {
/**
* 获取客户端可见内容的高度
*
* @returns {number}
*/
const getClientHeight = () => {
return window.innerHeight || Math.min(document.documentElement.clientHeight, document.body.clientHeight)
}
/**
* 获取客户端可见内容的宽度
*
* @returns {number}
*/
const getClientWidth = () => {
return window.innerWidth || Math.min(document.documentElement.clientWidth, document.body.clientWidth)
}
/**
* startX = null:获取鼠标相对于元素(左上顶点)的x轴坐标(移动前坐标)
* startX != null:获取移动后的左上顶点x轴坐标
*
* e.clientX:鼠标相对客户端(客户端左上顶点)的x轴坐标
* el.offsetLeft:元素顶点(左上顶点)相对客户端(客户端左上顶点)的x轴坐标(元素必须脱离文档流,position: fixed or absolute)
* el.clientWidth:元素宽度
*
* @param el
* @param e
* @param startX
* @returns {number}
*/
const getX = (el, e, startX) => {
if (startX === null) {
// 返回鼠标相对于元素(左上顶点)的x轴坐标
return e.clientX - el.offsetLeft
}
// 客户端可视宽度
const clientWidth = getClientWidth()
// 元素自身宽度
const elWidth = el.clientWidth
// 移动到x轴位置
let x = e.clientX - startX
// 水平方向边界处理
if (x <= 0) {
// x轴最小为0
x = 0
} else if (x + elWidth > clientWidth) {
// x是左上顶点的坐标,是否触碰到右边边界(超出可视宽度)要通过右顶点判断,所以需要加上元素自身宽度
x = clientWidth - elWidth
}
return x
}
/**
* startY = null:获取鼠标相对于元素(左上顶点)的y轴坐标(移动前坐标)
* startY != null:获取移动后的左上顶点y轴坐标
*
* e.clientY:鼠标相对客户端(客户端左上顶点)的y轴坐标
* el.offsetTop:元素顶点(左上顶点)相对客户端(客户端左上顶点)的y轴坐标(元素必须脱离文档流,position: fixed or absolute)
* el.clientHeight:元素高度
*
* @param el
* @param e
* @param startY
* @returns {number}
*/
const getY = (el, e, startY) => {
if (startY === null) {
// 返回鼠标相对于元素(左上顶点)的y轴坐标
return e.clientY - el.offsetTop
}
// 客户端可视高度
const clientHeight = getClientHeight()
// 元素自身高度
const elHeight = el.clientHeight
// 移动到y轴位置
let y = e.clientY - startY
// 垂直方向边界处理
if (y <= 0) {
// y轴最小为0
y = 0
} else if (y + elHeight > clientHeight) {
// 同理,判断是否超出可视高度要加上自身高度
y = clientHeight - elHeight
}
return y
}
/**
* 监听鼠标按下事件(PC端拖动)
*
* @param e
*/
el.onmousedown = (e) => {
vnode.context.isDrag = false
// 获取当前位置信息 (startX,startY)
const startX = getX(el, e, null)
const startY = getY(el, e, null)
/**
* 监听鼠标移动事件
*
* @param e
*/
document.onmousemove = (e) => {
// 标记正在移动,解决元素移动后点击事件被触发的问题
vnode.context.isDrag = true
// 更新元素位置(移动元素)
el.style.left = getX(el, e, startX) + 'px'
el.style.top = getY(el, e, startY) + 'px'
}
/**
* 监听鼠标松开事件
*/
document.onmouseup = () => {
// 移除鼠标相关事件,防止元素无法脱离鼠标
document.onmousemove = document.onmouseup = null
}
}
/**
* 监听手指按下事件(移动端拖动)
* @param e
*/
el.ontouchstart = (e) => {
// 获取被触摸的元素
const touch = e.targetTouches[0]
// 获取当前位置信息 (startX,startY)
const startX = getX(el, touch, null)
const startY = getY(el, touch, null)
/**
* 监听手指移动事件
* @param e
*/
document.ontouchmove = (e) => {
// 获取被触摸的元素
const touch = e.targetTouches[0]
// 更新元素位置(移动元素)
el.style.left = getX(el, touch, startX) + 'px'
el.style.top = getY(el, touch, startY) + 'px'
}
/**
* 监听手指移开事件
*/
document.ontouchend = () => {
// 移除touch相关事件,防止元素无法脱离手指
document.ontouchmove = document.ontouchend = null
}
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.ball-wrap {
position: fixed;
}
</style>drag 是我们自定义的指令,在需要滑动的元素上绑定 v-drag 即可。
注意
自定义指令this指向问题
在自定义指令 directives 内不能访问 this,如果需要修改 data 里的值,需要通过 vnode.context.字段名 = 值 修改。
滑动后点击事件被触发
鼠标事件触发顺序:
mouseover - mousedown - mouseup - click - mouseout
滑动的前提是鼠标必须按下再滑动,所以在我们滑动完毕松开鼠标时,click 事件会被触发。
解决方法:定义一个标志变量,表示是否是滑动,点击事件执行时,将此变量作为前置条件,如果是在滑动则不执行。
// ...
data()
return {
isDrag: false
}
}
// ...
el.onmousedown = (e) => {
// ...
vnode.context.isDrag = false
document.onmousemove = (e) => {
// 标记正在移动,解决元素移动后点击事件被触发的问题
vnode.context.isDrag = true
// ...
}
}
// ...
methods: {
click() {
if (this.isDrag) {
return
}
// ...
}
}移动端滑动问题
移动端滑动时会触发默认事件,导致滑动卡顿。
在要触发滑动的元素上加上 @touchmove.prevent,以阻止默认事件的发生。
源码
https://github.com/anlingyi/xeblog-vue/blob/master/src/components/xe-pokeball/index.vue
(学习视频分享:web前端开发、编程基础视频)
以上就是Vue实战:利用自定义指令实现鼠标拖动元素效果的详细内容,更多请关注其它相关文章!
