Python命令行定时任务自动化工作流程是什么
1.使用场景
定时执行jmeter脚本,通过python定时器隔一段时间执行命令行命令。
2.库
os、datetime、threading
(1)利用threading.Timer()定时器实现定时任务
| Timer方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Timer(interval, function, args=None, kwargs=None) | 创建定时器 |
| cancel() | 取消定时器 |
| start() | 使用线程方式执行 |
| join(self, timeout=None) | 等待线程执行结束 |
timer最基本理解就是定时器,可以启动多个定时任务,这些定时器任务是异步执行,所以不存在等待顺序执行问题。
3.运行脚本
jmeter执行命令行
jmeter -n -t 脚本名称.jmx -l 脚本报告名称.jtl
参数说明:
n 非GUI模式,命令行模式(表示在非GUI模式下运行)
-t 测试文件, 要运行的jmeter测试脚本文件(一般使用绝对路径)
-l 结果文件,记录结果的文件
-h 获取jmeter帮助信息
-r 远程执行,启动远程服务器(non-gui模式下启动remote-hosts配置的所有远程代理机)
-R 远程执行,(non-gui模式下启动指定的机器(IP:PORT)作为代理机)
-e 设置测试完成后生成测试报表
-o 指定测试报表生成的文件夹,文件夹必须为空/不存在
-H 代理主机(设置jmeter使用的代理主机)
-P 代理端口(设置jmeter使用的代理端口)
-X 退出(non-gui模式下测试结束时退出)
4.脚本
import os
from datetime import datetime
from threading import Timer
# 定时任务
def task():
now = datetime.now()
ts = now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
print(datetime.now())
a = os.system("jmeter -n -t /Users/liyinchi/workspace/功能测试/好慷/测试数据(压测脚本)/阶梯拼团多维表格20230418.jmx -l /Users/liyinchi/workspace/功能测试/好慷/测试数据(压测脚本)/阶梯拼团多维表格20230418-result.jtl")
print(a)
# 执行器
def func():
task()
t = Timer(60*1, func)
t.start()
func()执行结果:
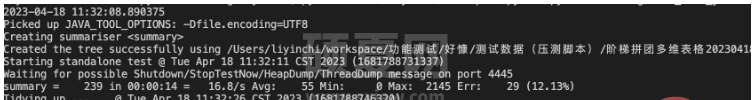
5.python常用的定时任务
while True:+sleep()
threading.Timer定时器
Timeloop库执行定时任务
调度模块sched
调度模块schedule
任务框架APScheduler
分布式消息系统celery执行定时任务
使用windows自带的定时任务
6.四种方法用python调用命令行
(1)os.system
import os
a=os.system("ls")
a运行程序会显示输出,返回值a为程序退出码
(2)os.popen
import os
a=os.popen("ls")
a.readline()返回值为一个file文件,
file.readlines()为命令的返回值
(3)subprocess
可以在python程序中创建子进程,
subprocess.call()
import subprocess subprocess.call(['ls','-l' ])
其中,'ls’对应命令行输入的命令,-l为相应的操作。返回程序退出码,类似于os.system
subprocess.check_output('ls')返回标准输出,类似于os.popen。
也可以调用Popen对象来进行操作。subprocess
import subprocess
child = subprocess.Popen('ping -c4 blog.linuxeye.com',shell=True)此时,可以用多个命令控制子进程。也可以用subprocess.PIPE,将自进程输入输出连接……
(4)commands
import commands
commands.getoutput('ls')返回程序输出
以上就是Python命令行定时任务自动化工作流程是什么的详细内容,更多请关注其它相关文章!
