java利用json文件来实现数据库数据的导入导出

背景:
工作中我们可能会遇到需要将某个环境中的某些数据快速的移动到另一个环境的情况,此时我们就可以通过导入导出json文件的方式实现。
(学习视频分享:java课程)
举例:
我们将这个环境的数据库中用户信息导出为一份json格式文件,再直接将json文件复制到另一个环境导入到数据库,这样可以达到我们的目的。
下面我将使用springboot搭建用户数据信息的导入导出案例,实现了单用户和多用户数据库信息的导入导出功能。认真看完这篇文章,你一定能掌握导入导出json文件的核心
准备工作
需要maven依赖坐标:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.29</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-mapper-asl</artifactId>
<version>1.9.13</version>
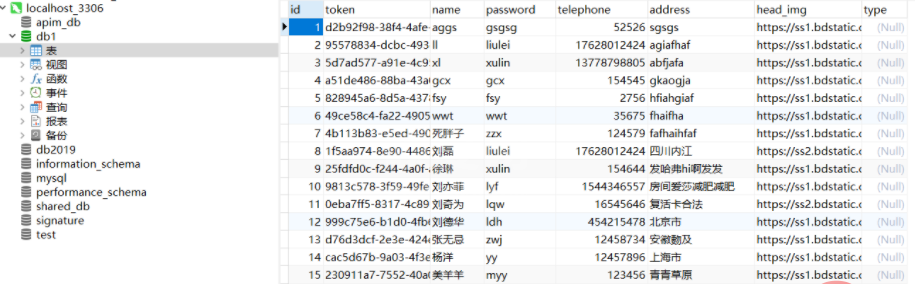
</dependency>数据库中的用户信息:
这些字段信息与Java中的UserEntity实体类一一对应
功能实现
准备好依赖和数据库信息之后,开始搭建用户导入导出具体框架:
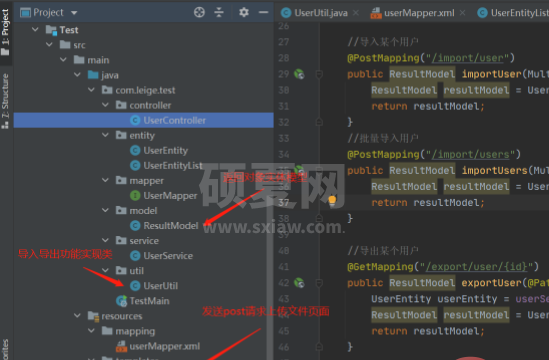
导入导出单用户、多用户功能实现 UserUtil
package com.leige.test.util;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import com.leige.test.entity.UserEntity;
import com.leige.test.entity.UserEntityList;
import com.leige.test.model.ResultModel;
import com.leige.test.service.UserService;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.codehaus.jackson.map.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.UUID;
public class UserUtil {
//导入用户
public static ResultModel importUser(MultipartFile multipartFile, UserService userService) {
ResultModel resultModel = new ResultModel();
try {
// 获取原始名字
String fileName = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
// 获取后缀名
String suffixName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//先将.json文件转为字符串类型
File file = new File("/"+ fileName);
//将MultipartFile类型转换为File类型
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(multipartFile.getInputStream(),file);
String jsonString = FileUtils.readFileToString(file, "UTF-8");
//如果是json或者txt文件
if (".json".equals(suffixName) || ".txt".equals(suffixName)) {
//再将json字符串转为实体类
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);
UserEntity userEntity = JSONObject.toJavaObject(jsonObject, UserEntity.class);
userEntity.setId(null);
userEntity.setToken(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
//调用创建用户的接口
userService.addUser(userEntity);
} else {
resultModel.setStatusCode(0);
resultModel.setStatusMes("请上传正确格式的.json或.txt文件!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return resultModel;
}
//批量导入用户
public static ResultModel importUsers(MultipartFile multipartFile, UserService userService) {
ResultModel resultModel = new ResultModel();
try {
// 获取原始名字
String fileName = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
// 获取后缀名
String suffixName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//先将.json文件转为字符串类型
File file = new File("/"+ fileName);
//将MultipartFile类型转换为File类型
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(multipartFile.getInputStream(),file);
String jsonString = FileUtils.readFileToString(file, "UTF-8");
//如果是json或者txt文件
if (".json".equals(suffixName) || ".txt".equals(suffixName)) {
//再将json字符串转为实体类
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);
UserEntityList userEntityList = JSONObject.toJavaObject(jsonObject, UserEntityList.class);
List<UserEntity> userEntities = userEntityList.getUserEntities();
for (UserEntity userEntity : userEntities) {
userEntity.setId(null);
userEntity.setToken(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
//调用创建用户的接口
userService.addUser(userEntity);
}
} else {
resultModel.setStatusCode(0);
resultModel.setStatusMes("请上传正确格式的.json或.txt文件!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return resultModel;
}
//导出某个用户
public static ResultModel exportUser(HttpServletResponse response, UserEntity userEntity, String fileName){
ResultModel resultModel = new ResultModel();
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(userEntity)){
resultModel.setStatusCode(0);
resultModel.setStatusMes("此用户id没有对应的用户");
return resultModel;
}else {
try {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(userEntity);
// 拼接文件完整路径// 生成json格式文件
String fullPath = "/" + fileName;
// 保证创建一个新文件
File file = new File(fullPath);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) { // 如果父目录不存在,创建父目录
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
if (file.exists()) { // 如果已存在,删除旧文件
file.delete();
}
file.createNewFile();//创建新文件
//将字符串格式化为json格式
jsonString = jsonFormat(jsonString);
// 将格式化后的字符串写入文件
Writer write = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file), "UTF-8");
write.write(jsonString);
write.flush();
write.close();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 设置相关格式
response.setContentType("application/force-download");
// 设置下载后的文件名以及header
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename="
.concat(String.valueOf(URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"))));
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 创建输出对象
OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
// 常规操作
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
os.write(buf, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
os.close(); //一定要记得关闭输出流,不然会继续写入返回实体模型
return resultModel;
} catch (Exception e) {
resultModel.setStatusCode(0);
resultModel.setStatusMes(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
return resultModel;
}
}
}
//导出所有用户
public static ResultModel exportAllUser(HttpServletResponse response, UserEntityList userEntityList, String fileName){
ResultModel resultModel = new ResultModel();
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(userEntityList)){
resultModel.setStatusCode(0);
resultModel.setStatusMes("此用户id没有对应的用户");
return resultModel;
}else {
try {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(userEntityList);
// 拼接文件完整路径// 生成json格式文件
String fullPath = "/" + fileName;
// 保证创建一个新文件
File file = new File(fullPath);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) { // 如果父目录不存在,创建父目录
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
if (file.exists()) { // 如果已存在,删除旧文件
file.delete();
}
file.createNewFile();//创建新文件
//将字符串格式化为json格式
jsonString = jsonFormat(jsonString);
// 将格式化后的字符串写入文件
Writer write = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file), "UTF-8");
write.write(jsonString);
write.flush();
write.close();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 设置相关格式
response.setContentType("application/force-download");
// 设置下载后的文件名以及header
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename="
.concat(String.valueOf(URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"))));
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 创建输出对象
OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
// 常规操作
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
os.write(buf, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
os.close(); //一定要记得关闭输出流,不然会继续写入返回实体模型
return resultModel;
} catch (Exception e) {
resultModel.setStatusCode(0);
resultModel.setStatusMes(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
return resultModel;
}
}
}
//将字符串格式化为json格式的字符串
public static String jsonFormat(String jsonString) {
JSONObject object= JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);
jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(object, SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat);
return jsonString;
}
}1、启动项目,浏览器输入访问 http://localhost:8888/export/users 导出所有已有用户json文件
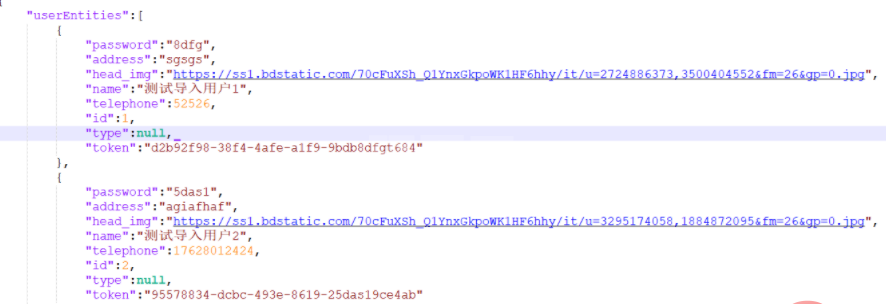
2、打开json文件查看格式是否正确

3、浏览器输入访问 http://localhost:8888/ 批量导入用户
导入 users.json 文件
输入地址,点击提交
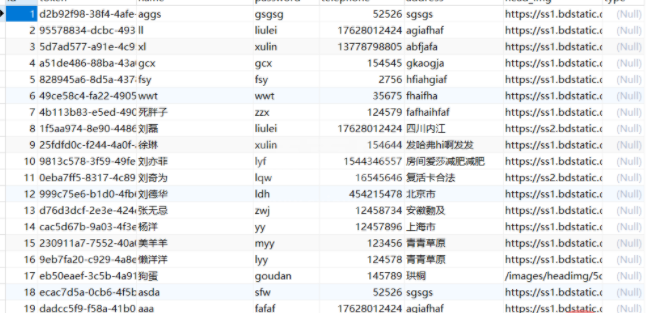
查看数据库,发现增加的两条测试用户1,2成功!
导入导出单个用户这里就不测试了,更加简单,其他的关于springboot配置文件和实体类对应数据库信息也不详细说明了。
相关推荐:java入门
以上就是java利用json文件来实现数据库数据的导入导出的详细内容,更多请关注其它相关文章!
