多线程 Cap 编程
主要技能和概念
• 了解创建多线程的基础知识
• 了解 thread 类和 runnable
接口
• 创建一个线程
• 创建多个线程
• 确定线程何时结束
• 使用线程优先级
• 了解线程同步
• 使用同步方法
• 使用同步块
• 促进线程之间的通信
• 暂停、恢复和停止线程
线程:这些是程序内独立的执行路径。
多任务:它可以基于进程(多个程序)或线程(同一程序中的多个任务)。
优点:
利用空闲时间提高效率。
更好地利用多核/多处理器系统。
线程创建和管理
类和接口:
thread:封装线程的类。
runnable:用于定义自定义线程的接口。
常用线程类方法:
- getname():返回线程的名称。
- getpriority():返回优先级。
- isalive():检查线程是否仍在执行。
- join():等待线程完成。
- run():定义线程的入口点。
- sleep(long ms):暂停线程一段时间。
- start(): 开始线程执行。
创建主题:
- 实现可运行:
class mythread implements runnable {
string threadname;
mythread(string name) {
threadname = name;
}
public void run() {
system.out.println(threadname + " starting.");
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
thread.sleep(400);
system.out.println("in " + threadname + ", count is " + i);
}
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
system.out.println(threadname + " interrupted.");
}
system.out.println(threadname + " terminating.");
}
}
public class usethreads {
public static void main(string[] args) {
system.out.println("main thread starting.");
mythread mythread = new mythread("child #1");
thread thread = new thread(mythread);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
system.out.print(".");
try {
thread.sleep(100);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
system.out.println("main thread interrupted.");
}
}
system.out.println("main thread ending.");
}
}
预期输出:
main thread starting. . child #1 starting. .. in child #1, count is 0 ... in child #1, count is 1 ... main thread ending.
线程类扩展:
class MyThread extends Thread { MyThread(String name) { super(name); } public void run() { System.out.println(getName() + " starting."); try { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Thread.sleep(400); System.out.println("In " + getName() + ", count is " + i); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(getName() + " interrupted."); } System.out.println(getName() + " terminating."); } } public class UseThreads { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Main thread starting."); MyThread thread = new MyThread("Child #1"); thread.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { System.out.print("."); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Main thread interrupted."); } } System.out.println("Main thread ending."); } }
注意:sleep()方法使得调用它的线程暂停执行
在指定的毫秒时间内。
书桌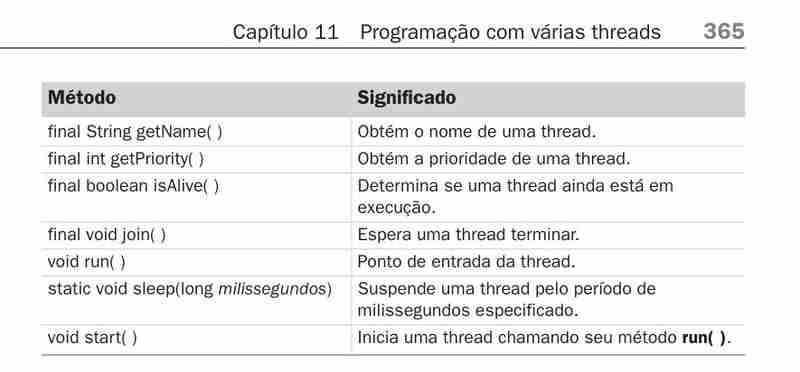
以上就是多线程 Cap 编程的详细内容,更多请关注硕下网其它相关文章!
